Install Ruby with Asdf
Here are instructions for installing Ruby using asdf, the software version manager. If you are not using asdf, you can see instructions to Install Ruby with frum or Install Ruby with Homebrew.
If you plan to use asdf, be sure you've completed the section, Install Asdf Version Manager.
Mac system Ruby
MacOS comes with a "system Ruby" pre-installed. MacOS Sonoma includes Ruby 2.6.10 which is not the newest version. It's a bad idea to use the Mac system Ruby. See the article Do not use the MacOS system Ruby. You can see the system Ruby with which ruby and ruby -v.
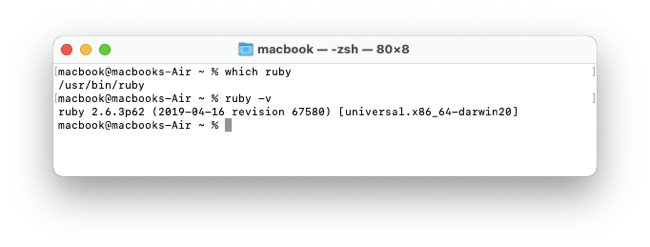
Leave the system Ruby in place and use the software version manager to install the newest Ruby version.
Install Ruby with Asdf
Check online for the current recommended version of Ruby.
When this was written, Ruby 3.4 was the newest version (3.4.1 was released on Dec 25, 2024).
First, install the asdf plugin for Ruby:
$ asdf plugin add ruby
See all the versions of Ruby that are available:
$ asdf list all ruby
If you don't see the newest version of Ruby, update the asdf plugin for Ruby and try again:
$ asdf plugin-update ruby
$ asdf list all ruby
Install the latest version of Ruby:
$ asdf install ruby latest
You’ll see diagnostic messages and progress updates. Installation takes less than five minutes on Apple Silicon with a fast Internet connection.
Asdf automatically installs OpenSSL which is a dependency for many Ruby gems.
You need to specify a default version of Ruby in your home ~/.tool-versions file. You can set the ~/.tool-versions file with a command:
$ asdf global ruby 3.4.1
🚩 Close and reopen the Terminal window for the changes to the ~/.zshrc file to be recognized. Alternatively (this is easier), you can use the source ~/.zshrc command to reset the shell environment.
Verify installation of Ruby
Verify that the newest version of Ruby is installed with ruby -v.
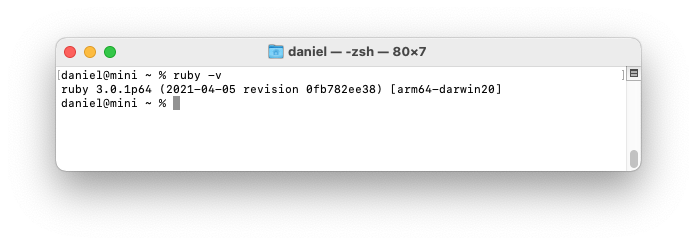
When this was written, Ruby 3.4.1 was the newest version (3.4.1 was released on Dec 25, 2024).
If you see Ruby version 2.6.10, it is the system Ruby and you likely forgot to close and re-open the terminal window.
If you see No version set for command ruby, you need to specify a default version of Ruby in your asdf ~/.tool-versions file.
If you don't see the latest version of Ruby, perhaps you installed Ruby previously with asdf and you need to reset the asdf ~/.tool-versions file.
Check for a ~/.tool-versions file.
$ cat ~/.tool-versions
Edit the ~/.tool-versions file (or create it if it doesn't exist) to set a default Ruby version.
ruby 3.4.1
The Uninstall Ruby section explains where Ruby versions are installed and how to remove them.
Next, you can optimize the Ruby development environment by updating gems. See the next section, Update Gems.
Using asdf as a version manager
You can install an earlier version of Ruby, for example Ruby 2.7.3.
$ asdf install ruby 2.7.3
For the current shell session, you can switch Ruby versions from the command line with asdf shell ruby 2.7.3. Opening the terminal will always use the default version of Ruby you specified initially with asdf global ruby 3.4.1.
The command asdf list ruby will show all installed versions of Ruby.
$ asdf list ruby
To override the default version of Ruby for a particular project, move into the project root directory and enter the command asdf local ruby <version>.
$ asdf local ruby 2.7.3
The command will write a file .tool-versions file in the current directory containing a Ruby version number.
The command asdf current will display all the asdf-installed software versions that are currently active.
If you no longer need a Ruby version, asdf can remove it with asdf uninstall ruby 2.7.3.